Find length of loop in linked list
int countNodes(struct Node *n)
{
int res = 1;
struct Node *temp = n;
while (temp->next != n)
{
res++;
temp = temp->next;
}
return res;
}
int countNodesinLoop(struct Node *list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next)
{
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
if (slow_p == fast_p)
return countNodes(slow_p);
}
return 0;
}
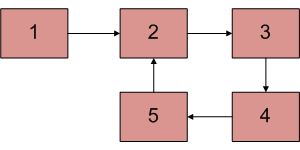
Write a function detectAndCountLoop() that checks whether a given Linked List contains loop and if loop is present then returns count of nodes in loop. For example, loop is present in below linked list and length of loop is 4. If loop is not present, then function should return 0.
We know that Floyd’s Cycle detection algorithm terminates when fast and slow pointers meet at a common point. We also know that this common point is one of the loop nodes (2 or 3 or 4 or 5 in the above diagram). We store the address of this in a pointer variable say ptr2. Then we start from the head of the Linked List and check for nodes one by one if they are reachable from ptr2. When we find a node that is reachable, we know that this node is the starting node of the loop in Linked List and we can get pointer to the previous of this node.
int countNodes(struct Node *n){ int res = 1; struct Node *temp = n; while (temp->next != n) { res++; temp = temp->next; } return res;}int countNodesinLoop(struct Node *list){ struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list; while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) { slow_p = slow_p->next; fast_p = fast_p->next->next; if (slow_p == fast_p) return countNodes(slow_p); } return 0;}
No comments:
Post a Comment